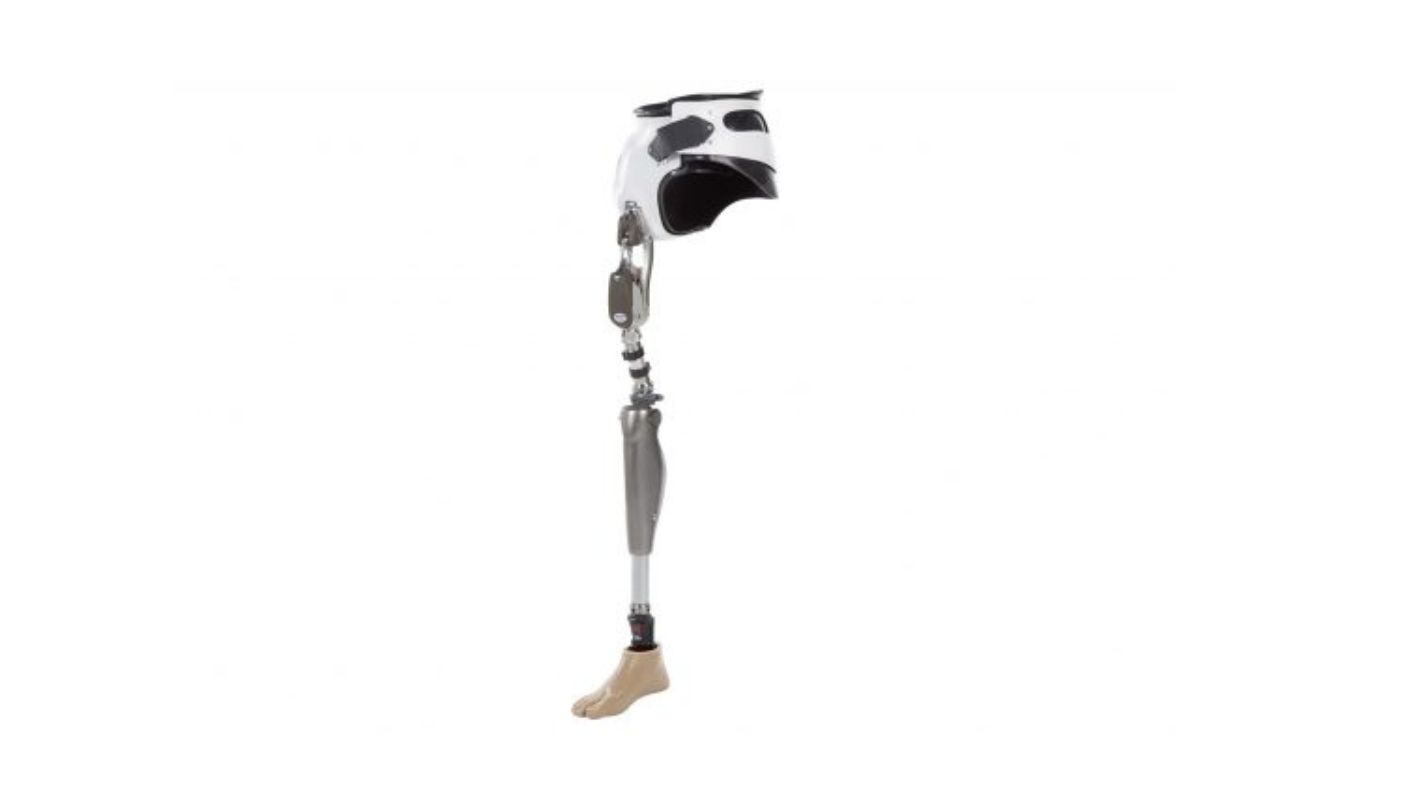
The hip joint component of the prosthesis is responsible for connecting the prosthetic limb
to the individual's body. It allows for rotation, flexion, and extension movements, enabling
the user to walk, sit, stand, and perform other daily activities. The hip joint is usually
adjustable to accommodate the user's comfort and movement requirements.
The knee joint component provides stability and mobility to the prosthetic limb. It allows
the knee to flex and extend, replicating the natural movement of a human knee. The choice of
knee joint depends on factors such as the individual's activity level and personal
preferences. The prosthetic foot component provides support, shock absorption, and
propulsion during weight-bearing activities. Different types of prosthetic feet are
available, tailored to the individual's mobility needs and lifestyle.
Overall, a hip disarticulation prosthesis aims to simulate the function of a natural leg,
restore mobility, and enhance the quality of life for individuals who have undergone a hip
disarticulation amputation. The design and features of the prosthesis may vary based on
individual needs, advancements in prosthetic technology, and the expertise of the
prosthetist involved in the fitting process. Consulting with a prosthetist or a healthcare
professional specializing in prosthetics is crucial to explore the possibilities and
determine the best options for an individual's specific situation.